| Lesson 6 | In-process COM servers: Registering and unregistering COM objects |
| Objective | Describe how an in-process server registers COM objects. |
In-process COM Servers: Registering and unregistering COM Objects
In-process COM servers provide the following required registry entries for each COM object they implement.| HKCR\CLSID\ {clsid} | Under HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID the COM object's CLSID, delimited by curly brackets ({}), is added as a key. For example:
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\ {5E533531-5EAC-11d2-85D9-08001700C57F}
Each COM object in a server is registered using a different CLSID. COM uses the CLSID registry entry to find the server that implements a specific COM object.
|
| HKCR\CLSID\{clsid} value | The value portion of the CLSID entry is optional.
Normally, applications put the name of the COM object in as the value. For example:
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\ {5E533531-5EAC-11d2-85D9-08001700C57F} = "MyComObject"
|
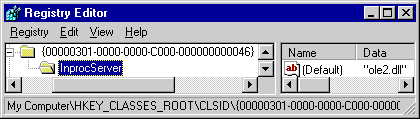
| HKCR\{clsid} \InprocServer32 | Under HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{ ... }, a subkey called InprocServer32 is added. For example:HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\ {5E533531-5EAC-11d2-85D9-08001700C57F}\ InprocServer32
|
| HKCR\CLSID\{clsid} \InprocServer32 value |
The value associated with the InprocServer32 key is the full directory path to the DLL housing the in-process server. For example:HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\ {5E533531-5EAC-11d2-85D9-08001700C57F}\ InprocServer32 = "c:\Dev\MyComObject\Debug\ComServer.dll"
|
| ProgID | Other optional entries include a ProgID. A ProgID is a string that can be used to look up an object's CLSID. |
| Exported functions | In-process servers implement two exported functions to support registering and unregistering COM classes,
DllRegisterServer and DllUnregisterServer (See below).
When DllRegisterServer is called, a server should register each COM object it implements. When DllUnregisterServer is called, a server should remove all entries for its COM
objects from the registry.
|
| Registration with RegSvr32 | Command-line tool RegSvr32.exe is used to register and unregister in-process servers.
Regedit.exe can be used to examine the contents of the registry. |
Implementing DllRegisterServer and DllUnregisterServer
DllRegisterServer can use Win32 API calls
Strings entered into the registry are "wide" strings, meaning that they are 16 bits per character.
Check the Win32 and COM documentation for details about the registry. Later on, we will develop a server using ATL. The ATL COM-Wizard will generate data and code that automatically handle registration for us.
RegCreatekeyEx and RegSetValueEx to add keys and values into the registry.
Strings entered into the registry are "wide" strings, meaning that they are 16 bits per character.
RegDeleteKey and RegDeleteValue can be used in DllUnregisterServer to remove a registry entry.
StringFromGUID2 takes in a CLSID in numeric format (for example, CLSID_O1) and converts it into a string.
GetModuleFileName gets the full path name of a module (for example, DLL) to enter as the InprocServer32 value.
Check the Win32 and COM documentation for details about the registry. Later on, we will develop a server using ATL. The ATL COM-Wizard will generate data and code that automatically handle registration for us.
Implementing DllRegisterServer
The final step is to implement the DllRegisterServer function.
The DLL that contains the component must export this function. The function will be called by a set-up application, or when the user runs the Regsvr32.exe tool. The following example in C++ shows a minimal implementation of DlLRegisterServer:
STDAPI DllRegisterServer(void){
return AMovieDllRegisterServer2(TRUE);
}
RegSvr32
| Register |
To register the COM classes (types of COM objects) implemented by a COM server, run RegSvr32 from the command line. It takes the name of the DLL, using full or relative path name, housing the in-process server as a command-line argument. RegSvr32 loads the DLL and calls DllRegisterServer. In response, the DLL registers its COM classes. For example, RegSvr32 MyComSvr.dll registers COM classes implemented in MyComSvr.dll.
|
| Unregister | To unregister a server's COM classes, run RegSvr32 using command-line flag /u, passing in the path to the DLL on the command line. RegSvr32 will load the DLL and call DllUnRegisterServer in the DLL. For example, RegSvr32 /u MyComSvr.dll
unregisters COM classes in MyComSvr.dll. RegSvr32 is usually found in the DevStudio\SharedIDE\bin directory. It may be in a different location on your system.
|
Regsvr32 is a command-line utility to register and unregister OLE controls, such as DLLs and ActiveX controls in the Windows Registry.
Regsvr32.exe is installed in the
The 64-bit version is %systemroot%\System32\regsvr32.exe.
The 32-bit version is %systemroot%\SysWoW64\regsvr32.exe.
Regsvr32.exe is installed in the
%systemroot%\System32 folder in Windows XP and later versions of Windows.Note On a 64-bit version of Windows operating system, there are two versions of the Regsv32.exe file:
The 64-bit version is %systemroot%\System32\regsvr32.exe.
The 32-bit version is %systemroot%\SysWoW64\regsvr32.exe.
Support for Windows XP has ended
Microsoft ended support for Windows XP on April 8, 2014. This change has affected your software updates and security options.
Microsoft ended support for Windows XP on April 8, 2014. This change has affected your software updates and security options.
In-process COM servers: Registering and unregistering COM objects
RegEdit is a registry browser and management tool. NT also had a tool known as RegEdt32.
The following diagram shows a COM object's entries.
COM-Objekt
Jeder Prozess, der ein COM-Objekt enthält, erhält dynamisch eine Portnummer zwischen 1024 und 65535. Das nachfolgende REGEDIT4-Listing zeigt die notwendigen Registry-Einträge, um die Ports einzuschränken. Im folgenden Beispiel werden nur die Ports 4000-6000 erlaubt.
REGEDIT4 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Rpc\Internet] "Ports"="4000-6000" "PortsInternetAvailable"="Y" "UseInternetPorts"="Y"Listing 3-6. Registry-Einstellungen zur Einschränkung der DCOM-Ports
dllCanUnloadNow - Exercise
Click the Exercise link below to apply what you have learned about COM server registry settings.
dllCanUnloadNow - Exercise
dllCanUnloadNow - Exercise